Define feasibility. Explain different categories of feasibility. How do you measure economic feasibility?
A feasibility study is a preliminary exploration of a proposed project or undertaking to determine its merits and viability. A feasibility study aims to provide an independent assessment that examines all aspects of a proposed project, including technical, economic, financial, legal, and environmental considerations.
- Technical Feasibility –
In Technical Feasibility current resources both hardware software along with required technology are analyzed/assessed to develop project. This technical feasibility study gives report whether there exists correct required resources and technologies which will be used for project development. Along with this, feasibility study also analyzes technical skills and capabilities of technical team, existing technology can be used or not, maintenance and up-gradation is easy or not for chosen technology etc. - Operational Feasibility –
In Operational Feasibility degree of providing service to requirements is analyzed along with how much easy product will be to operate and maintenance after deployment. Along with this other operational scopes are determining usability of product, Determining suggested solution by software development team is acceptable or not etc. - Economic Feasibility –
In Economic Feasibility study cost and benefit of the project is analyzed. Means under this feasibility study a detail analysis is carried out what will be cost of the project for development which includes all required cost for final development like hardware and software resource required, design and development cost and operational cost and so on. After that it is analyzed whether project will be beneficial in terms of finance for organization or not. - Legal Feasibility –
In Legal Feasibility study project is analyzed in legality point of view. This includes analyzing barriers of legal implementation of project, data protection acts or social media laws, project certificate, license, copyright etc. Overall it can be said that Legal Feasibility Study is study to know if proposed project conform legal and ethical requirements. - Schedule Feasibility –
In Schedule Feasibility Study mainly timelines/deadlines is analyzed for proposed project which includes how many times teams will take to complete final project which has a great impact on the organization as purpose of project may fail if it can’t be completed on time.
In Economic Feasibility study cost and benefit of the project is analyzed. Means under this feasibility study a detail analysis is carried out what will be cost of the project for development which includes all required cost for final development like hardware and software resource required, design and development cost and operational cost and so on. After that it is analyzed whether project will be beneficial in terms of finance for organization or not.
What is the waterfall model? Explain the prototyping model for developing information systems along with merits and demerits.
Waterfall Model is a sequential model that divides software development into pre-defined phases. Each phase must be completed before the next phase can begin with no overlap between the phases. Each phase is designed for performing specific activity during the SDLC phase. It was introduced in 1970 by Winston Royce.
The following illustration is a representation of the different phases of the Waterfall Model.

The prototyping Model is a software development model in which a prototype is built, tested, and reworked until an acceptable prototype is achieved. It also creates a base to produce the final system or software. It works best in scenarios where the project’s requirements are not known in detail. It is an iterative, trial-and-error method that takes place between the developer and the client.
Prototyping Model has following six SDLC phases as follow:
Step 1: Requirements gathering and analysis:
A prototyping model starts with requirement analysis. In this phase, the requirements of the system are defined in detail. During the process, the users of the system are interviewed to know what is their expectation from the system.
Step 2: Quick design:
The second phase is a preliminary design or a quick design. In this stage, a simple design of the system is created. However, it is not a complete design. It gives a brief idea of the system to the user. The quick design helps in developing the prototype.
Step 3: Build a Prototype:
In this phase, an actual prototype is designed based on the information gathered from quick design. It is a small working model of the required system.
Step 4: Initial user evaluation:
In this stage, the proposed system is presented to the client for an initial evaluation. It helps to find out the strength and weaknesses of the working model. Comments and suggestions are collected from the customer and provided to the developer.
Step 5: Refining prototype:
If the user is not happy with the current prototype, you need to refine the prototype according to the user’s feedback and suggestions.
This phase will not be over until all the requirements specified by the user are met. Once the user is satisfied with the developed prototype, a final system is developed based on the approved final prototype.
Step 6: Implement Product and Maintain:
Once the final system is developed based on the final prototype, it is thoroughly tested and deployed to production. The system undergoes routine maintenance for minimizing downtime and prevents large-scale failures.
Advantages of using the Prototype Model :
- This model is flexible in design.
- It is easy to detect errors.
- We can find missing functionality easily.
- There is a scope for refinement, which means new requirements can be easily accommodated.
- It can be reused by the developer for more complicated projects in the future.
Disadvantages of using the Prototype Model :
- This model is costly.
- It has poor documentation because of continuously changing customer requirements.
- There may be too much variation in requirements.
- Customers sometimes demand the actual product to be delivered soon after seeing an early prototype.
Assuming a retail clothing store in a mall, draw a context diagram and a level-0 diagram that represent the selling system at the store.


Explain the modern approach to system analysis and design.
System analysis and design are the complex, challenging, and simulating organization processes that a team of business and system professionals uses to develop and maintain computer-based information systems. It is an organizational improvement process. Information systems are built and rebuilt for their benefit.
1. Joint Application Design (JAD) :
JAD is a structured process in which users, managers and analysts work together for several days in a series of intensive meetings to specify or review system requirements. It is a management process – a people process – which allows IS to work more effectively with users in a shorter time frame. Because of bringing the people directly affected by the system in one place and time, time and organizational resources are better managed. Also, group members develop a shared understanding of what the system is supposed to do. The JAD process also includes approaches for enhancing user participation, expediting development, and improving the quality of specifications.

fig : Joint Application Design
Advantages :
- JAD decreases time and costs associated with requirements elicitation process.
- Creative idea production and improved user ownership of the system.
- Rapid development of systems.
Disadvantages :
- JAD requires a large block of time to be available for all session participants.
- Requires significant planning, scheduling effort and stakeholder commitment of time and effort.
- Requires trained and experienced personnel for facilitation and recording.
2. Agile model :
This model is an intuitive approach to the waterfall model. Multiple development cycles take place here, making the life cycle a “multi-waterfall” cycle. Cycles are divided up into smaller, more easily managed iterations. Each iteration passes through the requirements, design, implementation and testing phases. A working version ofsoftware is produced during the first iteration,so you have working software early on during the software life cycle. Subsequent iterations build on the initial software produced during the first iteration.

fig : Agile development Model
Advantages :
- In this model customer can respond to each built.
- More flexible – less costly to change scope and requirements.
- Easier to test and debug during a smaller iteration and manage risk because risky pieces are identified and handled during it’s iteration.
Disadvantages :
- Total cost is higher than waterfall.
- Needs a clear and complete definition of the whole system before it can be broken down and built incrementally.
Prototyping :
Prototyping is an iterative process of systems development in which requirements are converted to a working system that is continually revised through close work between an analyst and users. Designing and building a scaled-down but functional version of a desired system is the process known as prototyping. Prototyping is part of the analysis phase of the systems development life cycle. It is the process of building a model of a system.

fig : Prototype Development Model
Advantages :
- Useful for projects in which user requirements are uncertain or imprecise.
- It encourages active user and management participation.
- Projects have higher visibility and support because of the extensive user involvement.
Disadvantages :
- Incomplete or inadequate problem analysis.
- It increases lifetime cost to operate, support and maintain the system.
- Practically, this methodology may increase the complexity of the system as scope of the system may expand beyond original plans.
What is rapid application development? Explain.
The RAD (Rapid Application Development) model is based on prototyping and iterative development with no specific planning involved. The process of writing the software itself involves the planning required for developing the product. Rapid Application Development focuses on gathering customer requirements through workshops or focus groups, early testing of the prototypes by the customer using iterative concept, reuse of the existing prototypes (components), continuous integration and rapid delivery.
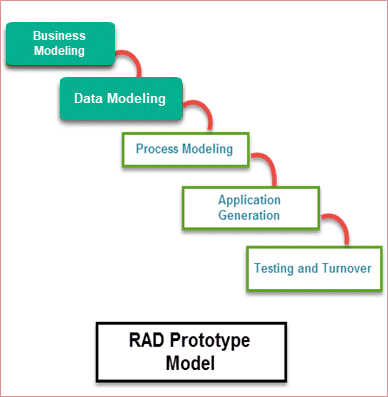
| RAD Model Phases | Activities performed in RAD Modeling |
|---|---|
| Business Modeling |
|
| Data Modeling |
|
| Process Modeling |
|
| Application Generation |
|
| Testing and Turnover |
|
What is project initiation? Explain different activities you will perform during project initiation phase.
Project initiation is the first phase of the project management life cycle and in this stage, companies decide if the project is needed and how beneficial it will be for them. The two metrics that are used to judge a proposed project and determine the expectations from it are the business case and feasibility study.
- To define the purpose and the expectations of the project.
- To define the project scope to ensure that the project covers all the required aspects and full addresses them.
- To define clear milestones and timeline for the project to ensure a smooth flow of events throughout the project.
- To devise the project’s deliverables that are in line with the goals and the clients expectations.
- To identify all the stakeholders that are to be directly or indirectly affected by the project.
- To come up with an enough budget – at this stage, a budget estimation is made for running the project.
- To establish the risks, issues and interdependencies connected to the project – this would help the team prepare and plan beforehand to avert the risks and tackle the issues.
What is the process of identifying and selecting information system development project in brief.
The Process of Identifying and Selecting Information Systems Development Projects
1. Identifying potential development projects. Organizations vary as to how they identify projects. This process can be performed by:
- A key member of top management, either the CEO of a small or medium-size organization or a senior executive in a larger organization
- A steering committee, composed of a cross section of managers with an interest in systems
- User departments, in which either the head of the requesting unit or a committee from the requesting department decides which projects to submit (as a systems analyst, you will help users prepare such requests)
- The development group or a senior IS manager
2. Classifying and ranking IS development projects. Assessing the merit of potential projects is the second major activity in the project identification and selection phase. As with project identification, classifying and ranking projects can be performed by top managers, a steering committee, business units, or the IS development group. The criteria used to assign the merit of a given project can vary based on the size of the organization. In any given organization, one or several criteria might be used during the classifying and ranking process
3. Selecting IS development projects. The selection of projects is the final activity in the project identification and selection phase. The short- and long-term projects most likely to achieve business objectives are considered. As business conditions change over time, the relative importance of any single project may substantially change. Thus, the identification and selection of projects is an important and ongoing activity.
Deliverables and Outcomes
The primary deliverable, or end product, from the project identification and selection phase is a schedule of specific IS development projects. These projects come from both top-down and bottom-up sources, and once selected they move into the second activity within this SDLC phase—project initiation and planning. An outcome of this activity is the assurance that people in the organization gave careful
What is a group interview? What are the benefits and drawbacks of group interviews?
Group Interview − In this type of interview, all the candidates or a group of candidates are interviewed together. Group interviews are conducted to save time when there is a large number of applications for a few job vacancies. A topic will be given to discuss among the candidates and the interviewer judges the innovativeness and behavior of each candidate in the group.
The benefits of group interviews are given below:
- Reduces both time and cost of hiring
- Opportunity to see candidate teamwork in action
- Gains a good understanding of candidates
The drawbacks of group interviews are given below:
- Conflict between candidates
- Not every personality type will thrive
- Only suitable for certain jobs
How do you format forms and reports? Explain general guidelines for formatting forms and reports.
Forms and reports are common ways to display and present data in a structured and organized manner. Proper formatting of forms and reports can improve readability, usability, and the overall user experience.
Here are some general guidelines for formatting forms and reports:
- Use consistent formatting: Consistency in formatting makes forms and reports look more professional and easier to read. Use the same font type, font size, and color scheme throughout the document.
- Align data: Aligning data elements such as labels and fields helps to organize the information and make it easier to read. Use a grid or table to align the data.
- Use white space: Use white space, or the empty space between data elements, to visually separate different sections of the form or report. This can make the document easier to read and less cluttered.
- Use headings: Use headings to break up the form or report into sections. This can help the user find the information they need more easily and quickly.
- Use color and graphics sparingly: Use color and graphics to highlight important information or to add visual interest to the form or report. However, use them sparingly as they can distract the user and make the document harder to read.
- Use clear and concise language: Use language that is clear, concise, and easy to understand. Avoid using technical jargon or complex words that the user may not understand.
- Consider the user: Design the form or report with the user in mind. Consider their needs and preferences and make sure the document is easy to navigate and use.
In summary, formatting forms and reports is an important aspect of presenting data in a clear and organized way. Use consistent formatting, align data, use white space, use headings, use color and graphics sparingly, use clear and concise language, and consider the user when designing the document.
List major activities of maintenance. Explain different types of maintenance activities.
Maintenance means restoring something to its original conditions. Enhancement means adding, modifying the code to support the changes in the user specification. System maintenance conforms the system to its original requirements and enhancement adds to system capability by incorporating new requirements.
Thus, maintenance changes the existing system, enhancement adds features to the existing system, and development replaces the existing system. It is an important part of system development that includes the activities which corrects errors in system design and implementation, updates the documents, and tests the data. For the purpose of convenience, maintenance may be categorized into three classes, namely:
i) Corrective Maintenance: This type of maintenance implies removing errors in a program, which might have crept in the system due to faulty design or wrong assumptions. Thus, in corrective maintenance, processing or performance failures are repaired.
ii) Adaptive Maintenance: In adaptive maintenance, program functions are changed to enable the information system to satisfy the information needs of the user. This type of maintenance may become necessary because of organizational changes which may include:
a) Change in the organizational procedures,
b) Change in organizational objectives, goals, policies, etc.
c) Change in forms,
d) Change in information needs of managers.
e) Change in system controls and security needs, etc.
iii)Perfective Maintenance: Perfective maintenance means adding new programs or modifying the existing programs to enhance the performance of the information system. This type of maintenance undertaken to respond to user’s additional needs which may be due to the changes within or outside of the organization. Outside changes are primarily environmental changes, which may in the absence of system maintenance, render the information system ineffective and inefficient. These environmental changes include:
a) Changes in governmental policies, laws, etc.,
b) Economic and competitive conditions, and
c) New technology.
What is object-oriented development? How is it different from structured development?
We know that the Object-Oriented Modelling (OOM) technique visualizes things in an application by using models organized around objects. Any software development approach goes through the following stages −
- Analysis,
- Design, and
- Implementation.
In object-oriented software engineering, the software developer identifies and organizes the application in terms of object-oriented concepts, prior to their final representation in any specific programming language or software tools.
Difference Between Structured and Object-oriented analysis :
| Structured Analysis | Object-Oriented Analysis |
|---|---|
| The main focus is on the process and procedures of the system. | The main focus is on data structure and real-world objects that are important. |
| It uses System Development Life Cycle (SDLC) methodology for different purposes like planning, analyzing, designing, implementing, and supporting an information system. | It uses Incremental or Iterative methodology to refine and extend our design. |
| It is suitable for well-defined projects with stable user requirements. | It is suitable for large projects with changing user requirements. |
| Risk while using this analysis technique is high and reusability is also low. | Risk while using this analysis technique is low and reusability is also high. |
| Structuring requirements include DFDs (Data Flow Diagram), Structured Analysis, ER (Entity Relationship) diagram, CFD (Control Flow Diagram), Data Dictionary, Decision table/tree, and the State transition diagram. | Requirement engineering includes the Use case model (find Use cases, Flow of events, Activity Diagram), the Object model (find Classes and class relations, Object interaction, Object to ER mapping), Statechart Diagram, and deployment diagram. |
| This technique is old and is not preferred usually. | This technique is new and is mostly preferred. |
Write short notes on
- Spiral model
- Decision table
a)
Spiral model is one of the most important Software Development Life Cycle models, which provides support for Risk Handling. In its diagrammatic representation, it looks like a spiral with many loops. The exact number of loops of the spiral is unknown and can vary from project to project. Each loop of the spiral is called a Phase of the software development process. The exact number of phases needed to develop the product can be varied by the project manager depending upon the project risks. As the project manager dynamically determines the number of phases, so the project manager has an important role to develop a product using the spiral model.
The Radius of the spiral at any point represents the expenses(cost) of the project so far, and the angular dimension represents the progress made so far in the current phase.
The below diagram shows the different phases of the Spiral Model: –
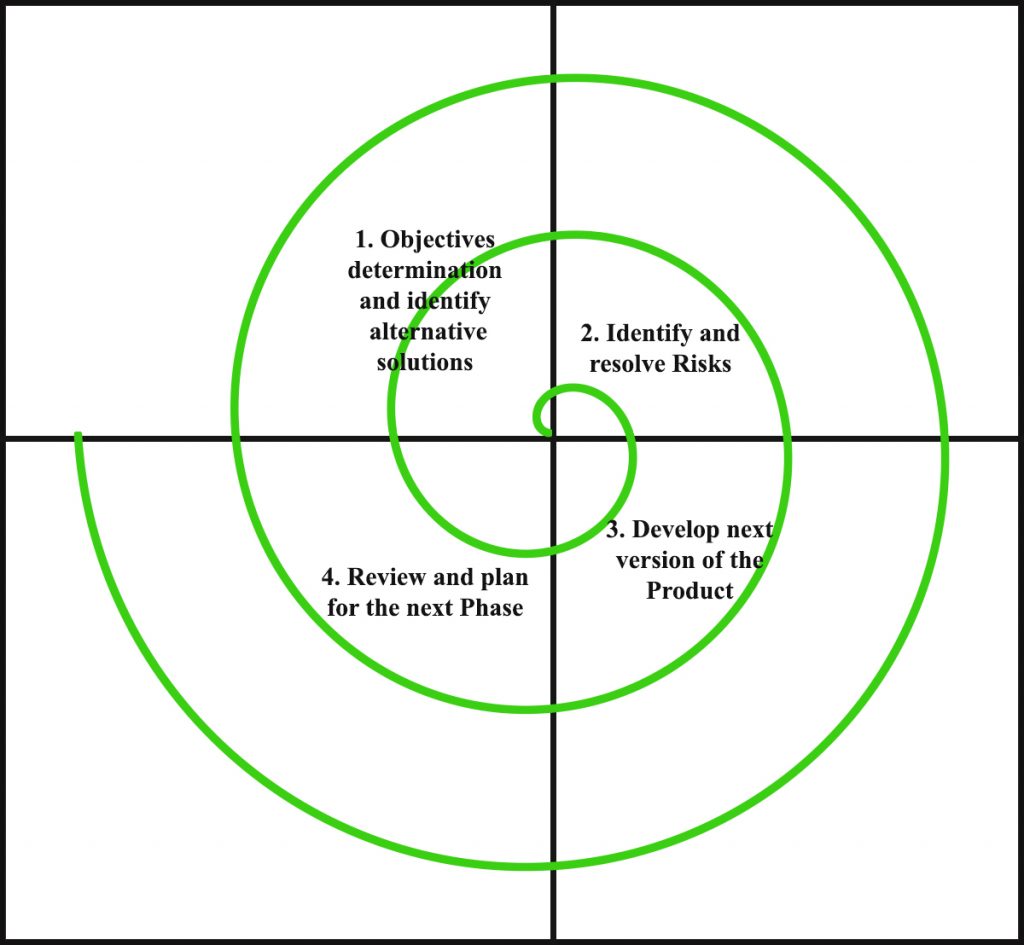
b)
A decision table is a brief visual representation for specifying which actions to perform depending on given conditions. The information represented in decision tables can also be represented as decision trees or in a programming language using if-then-else and switch-case statements.
A decision table is a good way to settle with different combination inputs with their corresponding outputs and is also called a cause-effect table. The reason to call cause-effect table is a related logical diagramming technique called cause-effect graphing that is basically used to obtain the decision table.
Importance of Decision Table:
- Decision tables are very much helpful in test design techniques.
- It helps testers to search the effects of combinations of different inputs and other software states that must correctly implement business rules.
- It provides a regular way of starting complex business rules, that is helpful for developers as well as for testers.
- It assists in the development process with the developer to do a better job. Testing with all combinations might be impractical.
- A decision table is basically an outstanding technique used in both testing and requirements management.